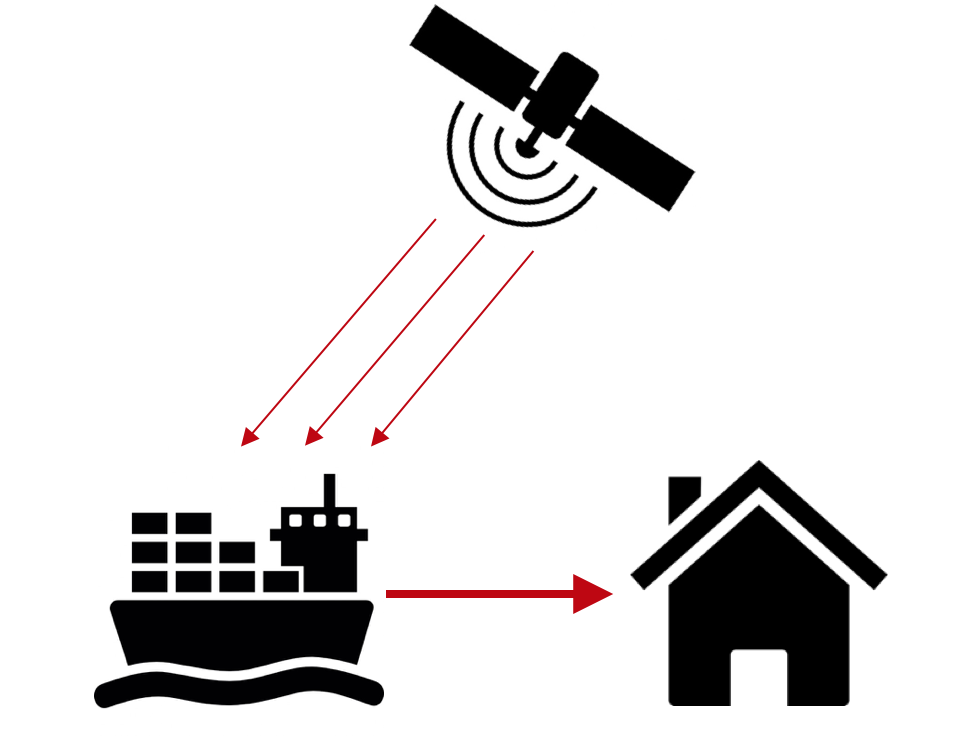
The Space to Sea Power Transmission system takes solar energy and uses it to provide power to victims in coastal cities after natural disasters. The system utilizes geostationary satellites to collect solar energy from 36,000km above the earth's surface. This energy is converted to microwaves and is beamed to one of our modified cargo ships. These modified ships each have a 100,000m2 circular rectenna array. This array absorbs the microwaves sent from the satellite, converts them to electricity using a rectenna array and stores it in Tesla Powerpacks on the ship. After a natural disaster, the ship can move close to the impacted area and deploy a smaller boat to bring the connecting cables to shore. Using a method similar to that of offshore wind turbines, the Powerpacks will send their power through the cable into the existing power grid, providing a constant and long-lasting supply of power to the affected area.


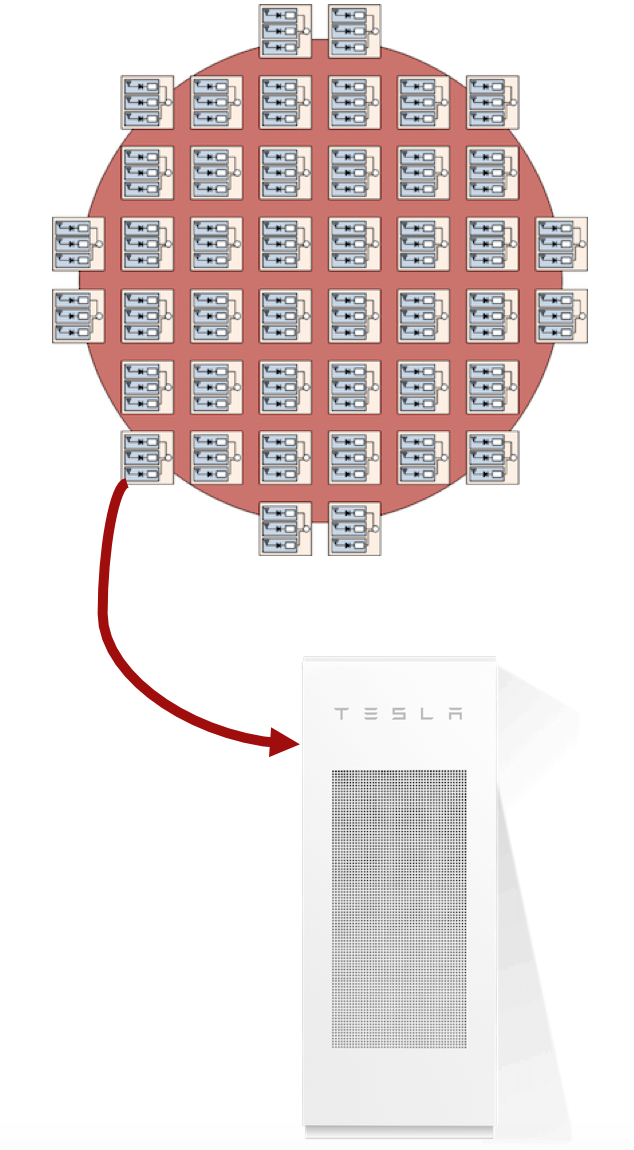

Energy Capacity: How much electricty can we can deliver?
The ship has 50,000 Powerpacks each rated for 210kWh
Each ship has a maximum energy capacity of 10.5 million kWh
A house running only neccessities needs 1350kWh per year; 3.69kWh per day
Therefore, one ship can support 2.8 million houses, given each home is only using the neccessities. This is only off the maximum storage of the ship. As power is transferred to the grid, the ship will capture more microwave energy and continue to store and supply more power
Sizes: How big is the system?
The satellite has a 1.6km2 solar cell array
The rectenna on the Maersk Triple E class ship is 100,000m2
As the conversion from microwaves to electricity is 85-90% efficient, the entire ship can charge in 8-12 hours (varies with temperature and weather conditions)
Cost: How much money is needed to fund this system?
SpaceX offers the cheapest viable launch service at $90 million per launch
A Maersk Triple E class ship costs $185 million USD
Manufacuturing costs for the satellite are around $350-400 million USD
Microwave radiation could be harmful to the crew. Faraday cages using metal mesh will be used to protect the crew from the microwaves.
Ion engines use xenon gas to position the satellite if micro adjustments are required. The microwave emitter may need to change its angle and this is done using an electric motor and energy from the solar cell array. The ship will run on diesel and will refuel when docked near land.
After anchoring, a smaller boat will deploy from the Triple E with the cable to connect to the grid. This will connect to the main grid using a messaging system to ensure the most efficient method of unloading the power is used.
As long as the local power grid is functional, this platform can integrate directly into it, requiring no modifications.
Geostationary satellite has 42% planetary coverage with a constant power supply, unhindered by atmospheric disturbances. There will be no satellite power supply during nighttime but the ship has enough stored power to keep the supply running until the satellite is able to start transmitting again.
One ship can cover the entire east or west coast of the United States in 5 days.
If the power supply lasts as long as predicted and does not cut out or fail in between, then it is a success. The goal of this process is to get the essential devices back online. This includes hospital, fire stations, police stations, and other essential needs. While our system likely will not be able to power an entire city, it can cover the areas that need electricity during the recovery process. If the system failed to contribute anything to the recovery effort, then it is a failure.